1)- Robert M. Bond, Christopher J. Fariss, Jason J. Jones, Adam D. I. Kramer, Cameron Marlow, Jaime E. Settle and James H. Fowler, “A 61-million-person experiment in social influence and political mobilization”
2)- Adam D. I. Kramer, Jamie E. Guillory, and Jeffrey T. Hancock, “Experimental evidence of massive-scale emotional contagion through social networks”
Summary:
Both papers examine social influence in online social networks (which is Facebook in both). The first paper studies if political behavior is contagious and can spread through an online social network, as it measures a social message on Facebook can influence users to vote during the US congressional election vs an informational message. They also measure the influence of friendship on Facebook in encouraging users to participate in the voting process. The second paper studies the emotional contagion on Facebook users and can controlling the percentage of emotional news and activities in the news feed could affect the Facebook user. Also both papers verify that the effects of face-to-face or non-verbal communications to propagate emotions and ideas are similar to those verbal/textual communication on social networks.
Reflection:
- In the first paper the authors divided their test groups into unbalanced three groups: the social message group (n = 60,055,176), the informational message group (n = 611,044) and the control group (n = 613,096). I do not know why they dedicated most of their test subjects to the first group (they did not give an explanation for that)
- The experiment in the second paper made me think that I have to read carefully the terms of use and privacy conditions of whatever social media I sign up to. Clearly the experiment is legal but is it ethical? Should Facebook experiment people and manipulate their emotions. I wounder what else they are testing?
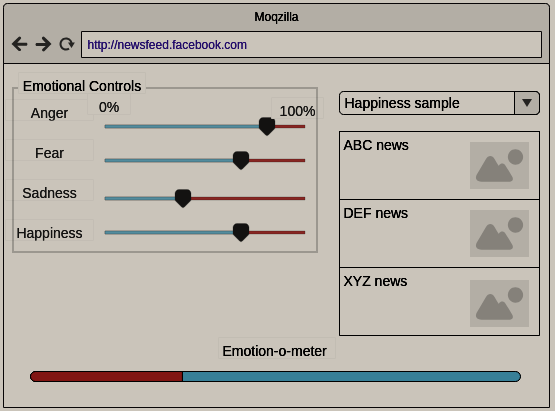
- Facebook news feed proved to be a powerful tool that can affect one’s emotions, mood and beliefs. I would like as a Facebook user some control over my news feed with respect to the type of emotions that the news hold. I would like to filter in/out posts and news related to my preferred mood. If this tool can classify the current post/activity into emotional/mood statuses and then later give the user the ability to control what to be displayed based on his/her target mood(s). This tool could also include an emotion-o-meter of the current news feed whether it is positive or negative or just normal news. This tool could help users maintain their well-being and mental health and measure how toxic their news feed is.
- In the second paper, the authors collected data for one week (January 11–18, 2012). I wonder if it was better if they collected data in some other period, since that time of the year is right after Christmas where people have recent positive emotions which might affect their online behavior and reaction to their news feeds.
- The second paper gave me an idea about enhancing the text-based sentiment analysis classifiers after adding emojis as features into the classification models